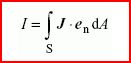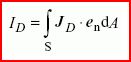-
1 courant de surface
сущ.радио. поверхностный токФранцузско-русский универсальный словарь > courant de surface
-
2 courant de surface
Dictionnaire français-russe de géographie > courant de surface
-
3 courant
* -
4 courant de conduction
ток проводимости
Явление направленного движения свободных носителей электрического заряда в веществе или в пустоте, количественно характеризуемое скалярной величиной, равной производной по времени от электрического заряда, переносимого свободными носителями заряда сквозь рассматриваемую поверхность.
[ ГОСТ Р 52002-2003]EN
(electric) current
(conduction) current
scalar quantity equal to the flux of the electric current density J through a given directed surface S:
where endA is the vector surface element
NOTE 1 – The electric current through a surface is equal to the limit of the quotient of the electric charge transferred through that surface during a time interval by the duration of this interval when this duration tends to zero.
NOTE 2 – For charge carriers confined to a surface, the electric current is defined through a curve of this surface (see the note to term “lineic electric current”).
[IEV number 121-11-13]FR
courant (électrique), m
courant (de conduction), m
grandeur scalaire égale au flux de la densité de courant électrique J à travers une surface orientée donnée S:
où endA est l'élément vectoriel de surface
NOTE 1 – Le courant électrique à travers une surface est égal à la limite du quotient de la charge électrique traversant cette surface pendant un intervalle de temps par la durée de cet intervalle lorsque cette durée tend vers zéro.
NOTE 2 – Pour des porteurs de charge confinés sur une surface, le courant électrique est défini à travers une courbe de cette surface (voir la note au terme "densité linéique de courant").
[IEV number 121-11-13]Тематики
- электротехника, основные понятия
Синонимы
EN
DE
- (elektrische) Stromstärke
- Leitungsstromstärke
- Stromstärke, (elektrische)
FR
Франко-русский словарь нормативно-технической терминологии > courant de conduction
-
5 courant électrique total
ток
Скалярная величина, равная сумме электрического тока проводимости, электрического тока переноса и электрического тока смещения сквозь рассматриваемую поверхность.
[ ГОСТ Р 52002-2003]EN
total electric current
scalar quantity given by the flux of the total current density Jt through a given directed surface S:
where endA is the vector surface element
NOTE – The total electric current It is given by
It = I + ID
where I is the electric current and ID the displacement current.
[IEV number 121-11-45]FR
courant électrique total, m
grandeur scalaire égale au flux de la densité de courant total Jt à travers une surface orientée donnée S:
où endA est l'élément vectoriel de surface
NOTE – Le courant électrique total It est donné par
It = I + ID
où I est le courant électrique et ID le courant de déplacement.
[IEV number 121-11-45]Тематики
- электротехника, основные понятия
Действия
- включать ток
- длительно пропускать ток
- коммутировать ток
- ограничивать ток
- отключать ток
- потреблять ток
- проводить ток
- пропускать ток
Синонимы
EN
DE
FR
Франко-русский словарь нормативно-технической терминологии > courant électrique total
-
6 courant de déplacement
ток смещения
Совокупность электрического тока смещения в пустоте и электрического тока поляризации, количественно характеризуемая скалярной величиной, равной производной по времени от потока электрического смещения сквозь рассматриваемую поверхность.
[ ГОСТ Р 52002-2003]EN
displacement current
scalar quantity equal to the flux of the displacement current density JD through a given directed surface S:
where endA is the vector surface element
[IEV number 121-11-43]FR
courant de déplacement, m
grandeur scalaire égale au flux de la densité de courant de déplacement JD à travers une surface orientée donnée S:
où endA est l'élément vectoriel de surface
[IEV number 121-11-43]Тематики
- электротехника, основные понятия
Синонимы
EN
DE
FR
Франко-русский словарь нормативно-технической терминологии > courant de déplacement
-
7 courant admissible, m
(длительный) допустимый ток
Максимальное значение электрического тока, который может протекать длительно по проводнику, устройству или аппарату при определенных условиях без превышения определенного значения их температуры в установившемся режиме
[ ГОСТ Р МЭК 60050-826-2009]
Этот ток обозначают IZ
[ ГОСТ Р 50571. 1-2009 ( МЭК 60364-1: 2005)]EN
(continuous) current-carrying capacity
ampacity (US)
maximum value of electric current which can be carried continuously by a conductor, a device or an apparatus, under specified conditions without its steady-state temperature exceeding a specified value
[IEV number 826-11-13]
ampacity
The current in amperes that a conductor can carry continuously under the conditions of use without exceeding its temperature rating.
[National Electrical Cod]FR
courant (permanent) admissible, m
valeur maximale du courant électrique qui peut parcourir en permanence, un conducteur, un dispositif ou un appareil, sans que sa température de régime permanent, dans des conditions données, soit supérieure à la valeur spécifiée
[IEV number 826-11-13]Ampacity, the term is defined as the maximum amount of current a cable can carry before sustaining immediate or progressive deterioration. Also described as current rating or current-carrying capacity, is the RMS electric current which a device can continuously carry while remaining within its temperature rating. The ampacity of a cable depends on:
- its insulation temperature rating;
- conductor electrical properties for current;
- frequency, in the case of alternating currents;
- ability to dissipate heat, which depends on cable geometry and its surroundings;
- ambient temperature.
Electric wires have some resistance, and electric current flowing through them causes voltage drop and power dissipation, which heats the cable. Copper or aluminum can conduct a large amount of current before melting, but long before the conductors melt, their insulation would be damaged by the heat.
The ampacity for a power cable is thus based on physical and electrical properties of the material & construction of the conductor and of its insulation, ambient temperature, and environmental conditions adjacent to the cable. Having a large overall surface area may dissipate heat well if the environment can absorb the heat.
In a long run of cable, different conditions govern, and installation regulations normally specify that the most severe condition along the run governs the cable's rating. Cables run in wet or oily locations may carry a lower temperature rating than in a dry installation. Derating is necessary for multiple circuits in close proximity. When multiple cables are near, each contributes heat to the others and diminishes the amount of cooling air that can flow past the individual cables. The overall ampacity of the insulated conductors in a bundle of more than 3 must be derated, whether in a raceway or cable. Usually the de-rating factor is tabulated in a nation's wiring regulations.
Depending on the type of insulating material, common maximum allowable temperatures at the surface of the conductor are 60, 75 and 90 degrees Celsius, often with an ambient air temperature of 30°C. In the U.S., 105°C is allowed with ambient of 40°C, for larger power cables, especially those operating at more than 2 kV. Likewise, specific insulations are rated 150, 200 or 250°C.
The allowed current in cables generally needs to be decreased (derated) when the cable is covered with fireproofing material.
For example, the United States National Electric Code, Table 310-16, specifies that up to three 8 AWG copper wires having a common insulating material (THWN) in a raceway, cable, or direct burial has an ampacity of 50 A when the ambient air is 30°C, the conductor surface temperature allowed to be 75°C. A single insulated conductor in air has 70 A rating.
Ampacity rating is normally for continuous current, and short periods of overcurrent occur without harm in most cabling systems. The acceptable magnitude and duration of overcurrent is a more complex topic than ampacity.
When designing an electrical system, one will normally need to know the current rating for the following:- Wires
- Printed Circuit Board traces, where included
- Fuses
- Circuit breakers
- All or nearly all components used
Some devices are limited by power rating, and when this power rating occurs below their current limit, it is not necessary to know the current limit to design a system. A common example of this is lightbulb holders.
[http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Ampacity]
Тематики
- электротехника, основные понятия
Синонимы
EN
DE
- Dauerstrombelastbarkeit, f
- Strombelastbarkeit, f
FR
- courant admissible, m
- courant permanent admissible, m
Франко-русский словарь нормативно-технической терминологии > courant admissible, m
-
8 courant permanent admissible, m
(длительный) допустимый ток
Максимальное значение электрического тока, который может протекать длительно по проводнику, устройству или аппарату при определенных условиях без превышения определенного значения их температуры в установившемся режиме
[ ГОСТ Р МЭК 60050-826-2009]
Этот ток обозначают IZ
[ ГОСТ Р 50571. 1-2009 ( МЭК 60364-1: 2005)]EN
(continuous) current-carrying capacity
ampacity (US)
maximum value of electric current which can be carried continuously by a conductor, a device or an apparatus, under specified conditions without its steady-state temperature exceeding a specified value
[IEV number 826-11-13]
ampacity
The current in amperes that a conductor can carry continuously under the conditions of use without exceeding its temperature rating.
[National Electrical Cod]FR
courant (permanent) admissible, m
valeur maximale du courant électrique qui peut parcourir en permanence, un conducteur, un dispositif ou un appareil, sans que sa température de régime permanent, dans des conditions données, soit supérieure à la valeur spécifiée
[IEV number 826-11-13]Ampacity, the term is defined as the maximum amount of current a cable can carry before sustaining immediate or progressive deterioration. Also described as current rating or current-carrying capacity, is the RMS electric current which a device can continuously carry while remaining within its temperature rating. The ampacity of a cable depends on:
- its insulation temperature rating;
- conductor electrical properties for current;
- frequency, in the case of alternating currents;
- ability to dissipate heat, which depends on cable geometry and its surroundings;
- ambient temperature.
Electric wires have some resistance, and electric current flowing through them causes voltage drop and power dissipation, which heats the cable. Copper or aluminum can conduct a large amount of current before melting, but long before the conductors melt, their insulation would be damaged by the heat.
The ampacity for a power cable is thus based on physical and electrical properties of the material & construction of the conductor and of its insulation, ambient temperature, and environmental conditions adjacent to the cable. Having a large overall surface area may dissipate heat well if the environment can absorb the heat.
In a long run of cable, different conditions govern, and installation regulations normally specify that the most severe condition along the run governs the cable's rating. Cables run in wet or oily locations may carry a lower temperature rating than in a dry installation. Derating is necessary for multiple circuits in close proximity. When multiple cables are near, each contributes heat to the others and diminishes the amount of cooling air that can flow past the individual cables. The overall ampacity of the insulated conductors in a bundle of more than 3 must be derated, whether in a raceway or cable. Usually the de-rating factor is tabulated in a nation's wiring regulations.
Depending on the type of insulating material, common maximum allowable temperatures at the surface of the conductor are 60, 75 and 90 degrees Celsius, often with an ambient air temperature of 30°C. In the U.S., 105°C is allowed with ambient of 40°C, for larger power cables, especially those operating at more than 2 kV. Likewise, specific insulations are rated 150, 200 or 250°C.
The allowed current in cables generally needs to be decreased (derated) when the cable is covered with fireproofing material.
For example, the United States National Electric Code, Table 310-16, specifies that up to three 8 AWG copper wires having a common insulating material (THWN) in a raceway, cable, or direct burial has an ampacity of 50 A when the ambient air is 30°C, the conductor surface temperature allowed to be 75°C. A single insulated conductor in air has 70 A rating.
Ampacity rating is normally for continuous current, and short periods of overcurrent occur without harm in most cabling systems. The acceptable magnitude and duration of overcurrent is a more complex topic than ampacity.
When designing an electrical system, one will normally need to know the current rating for the following:- Wires
- Printed Circuit Board traces, where included
- Fuses
- Circuit breakers
- All or nearly all components used
Some devices are limited by power rating, and when this power rating occurs below their current limit, it is not necessary to know the current limit to design a system. A common example of this is lightbulb holders.
[http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Ampacity]
Тематики
- электротехника, основные понятия
Синонимы
EN
DE
- Dauerstrombelastbarkeit, f
- Strombelastbarkeit, f
FR
- courant admissible, m
- courant permanent admissible, m
Франко-русский словарь нормативно-технической терминологии > courant permanent admissible, m
-
9 courant maximal admissible
допустимый длительный ток кабеля (провода)
-
[Интент]
допустимый длительный ток (проводника)
Максимальный электрический ток, который проводник способен проводить в продолжительном режиме без превышения его установившейся температурой определённого значения.
Допустимый длительный ток является одной из основных характеристик проводника. Он представляет собой максимальный электрический ток, который проводник может проводить длительно (неделями, месяцами, годами) не перегреваясь. Значение допустимого длительного тока зависит от сечения проводника, материалов из которых выполнены проводник и его изоляция, способов монтажа проводника в электроустановке здания. Допустимый длительный ток проводника фактически является его номинальным током. В электроустановках зданий выполняют защиту проводников от сверхтоков, протекание которых по проводникам сопровождается их перегревом.
[ http://www.volt-m.ru/glossary/letter/%C4/view/11/]EN
current carrying capacity
maximum current a cable circuit (one or several conductors) can support resulting in a specified increase of the surface temperature of the conductor beyond the ambient temperature, not exceeding the maximum allowed operating temperature of the cable
[IEC 61156-1, ed. 3.0 (2007-06< size="2">)]FR
courant maximal admissible
courant maximal qu’un circuit de câble (un ou plusieurs conducteurs) peut supporter avec une augmentation spécifiée de la température de surface du conducteur au delà de la température ambiante, et ne dépassant pas la température maximale de fonctionnement autorisée du câble
[IEC 61156-1, ed. 3.0 (2007-06< size="2">)]Номинальный ток устройств защиты от короткого замыкания может превышать допустимый длительный ток кабеля.
[ ГОСТ Р 50571. 5-94 ( МЭК 364-4-43-77)]Допустимые длительные токи для проводов и кабелей, проложенных в коробах, а также в лотках пучками, должны приниматься...
[ПУЭ]Тематики
- кабели, провода...
- электроустановки
EN
- ampere capacity
- current carrying capacity
- current carrying capacity of the cable
- current carrying capacity of the conductors
- current-carrying capacity of the cable
FR
Франко-русский словарь нормативно-технической терминологии > courant maximal admissible
-
10 courant de référence d'un parafoudre
классификационный ток ОПН
Iкл
Амплитудное значение (более высокое амплитудное значение из двух полярностей, если ток асимметричен) активной составляющей тока промышленной частоты, которое используется для определения классификационного напряжения ОПН и нормируется изготовителем.
[ ГОСТ Р 52725-2007]EN
reference current of an arrester
peak value (the higher peak value of the two polarities if the current is asymmetrical) of the resistive component of a power-frequency current used to determine the reference voltage of the arrester
NOTE 1 The reference current will be high enough to make the effects of stray capacitances at the measured reference voltage of the arrester units (with designed grading system) negligible and is to be specified by the manufacturer.
NOTE 2 Depending on the nominal discharge current and/or line discharge class of the arrester, the reference current will be typically in the range of 0,05 mA to 1,0 mA per square centimetre of disc area for single column arresters.
[IEC 60099-4, ed. 2.0 (2004-05)]FR
courant de référence d'un parafoudre
valeur de crête (la plus grande des deux polarités si le courant est dissymétrique) de la composante résistive du courant à fréquence industrielle utilisée pour déterminer la tension de référence d'un parafoudre.
NOTE 1 Il convient que le courant de référence soit suffisamment élevé pour rendre négligeables les effets des capacités parasites aux tensions de référence mesurées sur les éléments de parafoudre (avec leur système de répartition) et qu’il soit spécifié par le constructeur.
NOTE 2 Fonction du courant de décharge nominal et/ou de la classe de décharge de ligne du parafoudre, il convient que le courant de référence soit typiquement dans la gamme de 0,05 mA à 1,0 mA par centimètre carré de surface de disque pour les parafoudres à colonne unique
[IEC 60099-4, ed. 2.0 (2004-05)]Тематики
- высоковольтный аппарат, оборудование...
EN
FR
Франко-русский словарь нормативно-технической терминологии > courant de référence d'un parafoudre
-
11 revenir à la surface
(revenir à la [или en] (remonter à la, faire retour à la, refaire) surface)À mi-parcours, je tournais la tête en arrière, pour regarder de combien je l'avais distancée. Elle se débattait dans un remous, coula, refit surface avec peine, presque suffoquée. Le courant l'emporta. (D. Fernandez, Dans la main de l'ange.) — На полпути я обернулся назад, чтобы посмотреть, насколько я обогнал ее. Она барахталась в волнах, потом исчезла, с трудом всплыла, почти обессиленная. Ее унесло течением.
2) разг. оправиться, прийти в себяMais c'est quand même bête de se laisser démolir chaque fois par une Marie, et de chaque fois devoir remonter à la surface. (R. Pinget, Quelqu'un.) — Все же это глупо позволять себе расстраиваться то и дело из-за какой-то Мари, и каждый раз потом стараться восстановить равновесие.
3) разг. вновь всплыть, вновь появиться в обществе ( после периода отсутствия)Après tout, j'étais heureux d'être revenu à la surface, fût-ce d'un discours, d'exister à nouveau, d'avoir un nom. (S. Borgeaud, Le Voyage à l'étranger.) — В конце концов я был счастлив, что обо мне вспомнили, хотя бы в разговоре, что я опять для них существую, что у меня есть свое имя.
Dictionnaire français-russe des idiomes > revenir à la surface
-
12 (elektrische) Stromstärke
ток проводимости
Явление направленного движения свободных носителей электрического заряда в веществе или в пустоте, количественно характеризуемое скалярной величиной, равной производной по времени от электрического заряда, переносимого свободными носителями заряда сквозь рассматриваемую поверхность.
[ ГОСТ Р 52002-2003]EN
(electric) current
(conduction) current
scalar quantity equal to the flux of the electric current density J through a given directed surface S:
where endA is the vector surface element
NOTE 1 – The electric current through a surface is equal to the limit of the quotient of the electric charge transferred through that surface during a time interval by the duration of this interval when this duration tends to zero.
NOTE 2 – For charge carriers confined to a surface, the electric current is defined through a curve of this surface (see the note to term “lineic electric current”).
[IEV number 121-11-13]FR
courant (électrique), m
courant (de conduction), m
grandeur scalaire égale au flux de la densité de courant électrique J à travers une surface orientée donnée S:
où endA est l'élément vectoriel de surface
NOTE 1 – Le courant électrique à travers une surface est égal à la limite du quotient de la charge électrique traversant cette surface pendant un intervalle de temps par la durée de cet intervalle lorsque cette durée tend vers zéro.
NOTE 2 – Pour des porteurs de charge confinés sur une surface, le courant électrique est défini à travers une courbe de cette surface (voir la note au terme "densité linéique de courant").
[IEV number 121-11-13]Тематики
- электротехника, основные понятия
Синонимы
EN
DE
- (elektrische) Stromstärke
- Leitungsstromstärke
- Stromstärke, (elektrische)
FR
Немецко-русский словарь нормативно-технической терминологии > (elektrische) Stromstärke
-
13 Leitungsstromstärke
ток проводимости
Явление направленного движения свободных носителей электрического заряда в веществе или в пустоте, количественно характеризуемое скалярной величиной, равной производной по времени от электрического заряда, переносимого свободными носителями заряда сквозь рассматриваемую поверхность.
[ ГОСТ Р 52002-2003]EN
(electric) current
(conduction) current
scalar quantity equal to the flux of the electric current density J through a given directed surface S:
where endA is the vector surface element
NOTE 1 – The electric current through a surface is equal to the limit of the quotient of the electric charge transferred through that surface during a time interval by the duration of this interval when this duration tends to zero.
NOTE 2 – For charge carriers confined to a surface, the electric current is defined through a curve of this surface (see the note to term “lineic electric current”).
[IEV number 121-11-13]FR
courant (électrique), m
courant (de conduction), m
grandeur scalaire égale au flux de la densité de courant électrique J à travers une surface orientée donnée S:
où endA est l'élément vectoriel de surface
NOTE 1 – Le courant électrique à travers une surface est égal à la limite du quotient de la charge électrique traversant cette surface pendant un intervalle de temps par la durée de cet intervalle lorsque cette durée tend vers zéro.
NOTE 2 – Pour des porteurs de charge confinés sur une surface, le courant électrique est défini à travers une courbe de cette surface (voir la note au terme "densité linéique de courant").
[IEV number 121-11-13]Тематики
- электротехника, основные понятия
Синонимы
EN
DE
- (elektrische) Stromstärke
- Leitungsstromstärke
- Stromstärke, (elektrische)
FR
Немецко-русский словарь нормативно-технической терминологии > Leitungsstromstärke
-
14 Stromstärke, (elektrische)
ток проводимости
Явление направленного движения свободных носителей электрического заряда в веществе или в пустоте, количественно характеризуемое скалярной величиной, равной производной по времени от электрического заряда, переносимого свободными носителями заряда сквозь рассматриваемую поверхность.
[ ГОСТ Р 52002-2003]EN
(electric) current
(conduction) current
scalar quantity equal to the flux of the electric current density J through a given directed surface S:
where endA is the vector surface element
NOTE 1 – The electric current through a surface is equal to the limit of the quotient of the electric charge transferred through that surface during a time interval by the duration of this interval when this duration tends to zero.
NOTE 2 – For charge carriers confined to a surface, the electric current is defined through a curve of this surface (see the note to term “lineic electric current”).
[IEV number 121-11-13]FR
courant (électrique), m
courant (de conduction), m
grandeur scalaire égale au flux de la densité de courant électrique J à travers une surface orientée donnée S:
où endA est l'élément vectoriel de surface
NOTE 1 – Le courant électrique à travers une surface est égal à la limite du quotient de la charge électrique traversant cette surface pendant un intervalle de temps par la durée de cet intervalle lorsque cette durée tend vers zéro.
NOTE 2 – Pour des porteurs de charge confinés sur une surface, le courant électrique est défini à travers une courbe de cette surface (voir la note au terme "densité linéique de courant").
[IEV number 121-11-13]Тематики
- электротехника, основные понятия
Синонимы
EN
DE
- (elektrische) Stromstärke
- Leitungsstromstärke
- Stromstärke, (elektrische)
FR
Немецко-русский словарь нормативно-технической терминологии > Stromstärke, (elektrische)
-
15 conduction current
ток проводимости
Явление направленного движения свободных носителей электрического заряда в веществе или в пустоте, количественно характеризуемое скалярной величиной, равной производной по времени от электрического заряда, переносимого свободными носителями заряда сквозь рассматриваемую поверхность.
[ ГОСТ Р 52002-2003]EN
(electric) current
(conduction) current
scalar quantity equal to the flux of the electric current density J through a given directed surface S:
where endA is the vector surface element
NOTE 1 – The electric current through a surface is equal to the limit of the quotient of the electric charge transferred through that surface during a time interval by the duration of this interval when this duration tends to zero.
NOTE 2 – For charge carriers confined to a surface, the electric current is defined through a curve of this surface (see the note to term “lineic electric current”).
[IEV number 121-11-13]FR
courant (électrique), m
courant (de conduction), m
grandeur scalaire égale au flux de la densité de courant électrique J à travers une surface orientée donnée S:
où endA est l'élément vectoriel de surface
NOTE 1 – Le courant électrique à travers une surface est égal à la limite du quotient de la charge électrique traversant cette surface pendant un intervalle de temps par la durée de cet intervalle lorsque cette durée tend vers zéro.
NOTE 2 – Pour des porteurs de charge confinés sur une surface, le courant électrique est défini à travers une courbe de cette surface (voir la note au terme "densité linéique de courant").
[IEV number 121-11-13]Тематики
- электротехника, основные понятия
Синонимы
EN
DE
- (elektrische) Stromstärke
- Leitungsstromstärke
- Stromstärke, (elektrische)
FR
Англо-русский словарь нормативно-технической терминологии > conduction current
-
16 Gesamtstromstärke
ток
Скалярная величина, равная сумме электрического тока проводимости, электрического тока переноса и электрического тока смещения сквозь рассматриваемую поверхность.
[ ГОСТ Р 52002-2003]EN
total electric current
scalar quantity given by the flux of the total current density Jt through a given directed surface S:
where endA is the vector surface element
NOTE – The total electric current It is given by
It = I + ID
where I is the electric current and ID the displacement current.
[IEV number 121-11-45]FR
courant électrique total, m
grandeur scalaire égale au flux de la densité de courant total Jt à travers une surface orientée donnée S:
où endA est l'élément vectoriel de surface
NOTE – Le courant électrique total It est donné par
It = I + ID
où I est le courant électrique et ID le courant de déplacement.
[IEV number 121-11-45]Тематики
- электротехника, основные понятия
Действия
- включать ток
- длительно пропускать ток
- коммутировать ток
- ограничивать ток
- отключать ток
- потреблять ток
- проводить ток
- пропускать ток
Синонимы
EN
DE
FR
Немецко-русский словарь нормативно-технической терминологии > Gesamtstromstärke
-
17 total electric current
ток
Скалярная величина, равная сумме электрического тока проводимости, электрического тока переноса и электрического тока смещения сквозь рассматриваемую поверхность.
[ ГОСТ Р 52002-2003]EN
total electric current
scalar quantity given by the flux of the total current density Jt through a given directed surface S:
where endA is the vector surface element
NOTE – The total electric current It is given by
It = I + ID
where I is the electric current and ID the displacement current.
[IEV number 121-11-45]FR
courant électrique total, m
grandeur scalaire égale au flux de la densité de courant total Jt à travers une surface orientée donnée S:
où endA est l'élément vectoriel de surface
NOTE – Le courant électrique total It est donné par
It = I + ID
où I est le courant électrique et ID le courant de déplacement.
[IEV number 121-11-45]Тематики
- электротехника, основные понятия
Действия
- включать ток
- длительно пропускать ток
- коммутировать ток
- ограничивать ток
- отключать ток
- потреблять ток
- проводить ток
- пропускать ток
Синонимы
EN
DE
FR
Англо-русский словарь нормативно-технической терминологии > total electric current
-
18 Dauerstrombelastbarkeit, f
(длительный) допустимый ток
Максимальное значение электрического тока, который может протекать длительно по проводнику, устройству или аппарату при определенных условиях без превышения определенного значения их температуры в установившемся режиме
[ ГОСТ Р МЭК 60050-826-2009]
Этот ток обозначают IZ
[ ГОСТ Р 50571. 1-2009 ( МЭК 60364-1: 2005)]EN
(continuous) current-carrying capacity
ampacity (US)
maximum value of electric current which can be carried continuously by a conductor, a device or an apparatus, under specified conditions without its steady-state temperature exceeding a specified value
[IEV number 826-11-13]
ampacity
The current in amperes that a conductor can carry continuously under the conditions of use without exceeding its temperature rating.
[National Electrical Cod]FR
courant (permanent) admissible, m
valeur maximale du courant électrique qui peut parcourir en permanence, un conducteur, un dispositif ou un appareil, sans que sa température de régime permanent, dans des conditions données, soit supérieure à la valeur spécifiée
[IEV number 826-11-13]Ampacity, the term is defined as the maximum amount of current a cable can carry before sustaining immediate or progressive deterioration. Also described as current rating or current-carrying capacity, is the RMS electric current which a device can continuously carry while remaining within its temperature rating. The ampacity of a cable depends on:
- its insulation temperature rating;
- conductor electrical properties for current;
- frequency, in the case of alternating currents;
- ability to dissipate heat, which depends on cable geometry and its surroundings;
- ambient temperature.
Electric wires have some resistance, and electric current flowing through them causes voltage drop and power dissipation, which heats the cable. Copper or aluminum can conduct a large amount of current before melting, but long before the conductors melt, their insulation would be damaged by the heat.
The ampacity for a power cable is thus based on physical and electrical properties of the material & construction of the conductor and of its insulation, ambient temperature, and environmental conditions adjacent to the cable. Having a large overall surface area may dissipate heat well if the environment can absorb the heat.
In a long run of cable, different conditions govern, and installation regulations normally specify that the most severe condition along the run governs the cable's rating. Cables run in wet or oily locations may carry a lower temperature rating than in a dry installation. Derating is necessary for multiple circuits in close proximity. When multiple cables are near, each contributes heat to the others and diminishes the amount of cooling air that can flow past the individual cables. The overall ampacity of the insulated conductors in a bundle of more than 3 must be derated, whether in a raceway or cable. Usually the de-rating factor is tabulated in a nation's wiring regulations.
Depending on the type of insulating material, common maximum allowable temperatures at the surface of the conductor are 60, 75 and 90 degrees Celsius, often with an ambient air temperature of 30°C. In the U.S., 105°C is allowed with ambient of 40°C, for larger power cables, especially those operating at more than 2 kV. Likewise, specific insulations are rated 150, 200 or 250°C.
The allowed current in cables generally needs to be decreased (derated) when the cable is covered with fireproofing material.
For example, the United States National Electric Code, Table 310-16, specifies that up to three 8 AWG copper wires having a common insulating material (THWN) in a raceway, cable, or direct burial has an ampacity of 50 A when the ambient air is 30°C, the conductor surface temperature allowed to be 75°C. A single insulated conductor in air has 70 A rating.
Ampacity rating is normally for continuous current, and short periods of overcurrent occur without harm in most cabling systems. The acceptable magnitude and duration of overcurrent is a more complex topic than ampacity.
When designing an electrical system, one will normally need to know the current rating for the following:- Wires
- Printed Circuit Board traces, where included
- Fuses
- Circuit breakers
- All or nearly all components used
Some devices are limited by power rating, and when this power rating occurs below their current limit, it is not necessary to know the current limit to design a system. A common example of this is lightbulb holders.
[http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Ampacity]
Тематики
- электротехника, основные понятия
Синонимы
EN
DE
- Dauerstrombelastbarkeit, f
- Strombelastbarkeit, f
FR
- courant admissible, m
- courant permanent admissible, m
Немецко-русский словарь нормативно-технической терминологии > Dauerstrombelastbarkeit, f
-
19 Strombelastbarkeit, f
(длительный) допустимый ток
Максимальное значение электрического тока, который может протекать длительно по проводнику, устройству или аппарату при определенных условиях без превышения определенного значения их температуры в установившемся режиме
[ ГОСТ Р МЭК 60050-826-2009]
Этот ток обозначают IZ
[ ГОСТ Р 50571. 1-2009 ( МЭК 60364-1: 2005)]EN
(continuous) current-carrying capacity
ampacity (US)
maximum value of electric current which can be carried continuously by a conductor, a device or an apparatus, under specified conditions without its steady-state temperature exceeding a specified value
[IEV number 826-11-13]
ampacity
The current in amperes that a conductor can carry continuously under the conditions of use without exceeding its temperature rating.
[National Electrical Cod]FR
courant (permanent) admissible, m
valeur maximale du courant électrique qui peut parcourir en permanence, un conducteur, un dispositif ou un appareil, sans que sa température de régime permanent, dans des conditions données, soit supérieure à la valeur spécifiée
[IEV number 826-11-13]Ampacity, the term is defined as the maximum amount of current a cable can carry before sustaining immediate or progressive deterioration. Also described as current rating or current-carrying capacity, is the RMS electric current which a device can continuously carry while remaining within its temperature rating. The ampacity of a cable depends on:
- its insulation temperature rating;
- conductor electrical properties for current;
- frequency, in the case of alternating currents;
- ability to dissipate heat, which depends on cable geometry and its surroundings;
- ambient temperature.
Electric wires have some resistance, and electric current flowing through them causes voltage drop and power dissipation, which heats the cable. Copper or aluminum can conduct a large amount of current before melting, but long before the conductors melt, their insulation would be damaged by the heat.
The ampacity for a power cable is thus based on physical and electrical properties of the material & construction of the conductor and of its insulation, ambient temperature, and environmental conditions adjacent to the cable. Having a large overall surface area may dissipate heat well if the environment can absorb the heat.
In a long run of cable, different conditions govern, and installation regulations normally specify that the most severe condition along the run governs the cable's rating. Cables run in wet or oily locations may carry a lower temperature rating than in a dry installation. Derating is necessary for multiple circuits in close proximity. When multiple cables are near, each contributes heat to the others and diminishes the amount of cooling air that can flow past the individual cables. The overall ampacity of the insulated conductors in a bundle of more than 3 must be derated, whether in a raceway or cable. Usually the de-rating factor is tabulated in a nation's wiring regulations.
Depending on the type of insulating material, common maximum allowable temperatures at the surface of the conductor are 60, 75 and 90 degrees Celsius, often with an ambient air temperature of 30°C. In the U.S., 105°C is allowed with ambient of 40°C, for larger power cables, especially those operating at more than 2 kV. Likewise, specific insulations are rated 150, 200 or 250°C.
The allowed current in cables generally needs to be decreased (derated) when the cable is covered with fireproofing material.
For example, the United States National Electric Code, Table 310-16, specifies that up to three 8 AWG copper wires having a common insulating material (THWN) in a raceway, cable, or direct burial has an ampacity of 50 A when the ambient air is 30°C, the conductor surface temperature allowed to be 75°C. A single insulated conductor in air has 70 A rating.
Ampacity rating is normally for continuous current, and short periods of overcurrent occur without harm in most cabling systems. The acceptable magnitude and duration of overcurrent is a more complex topic than ampacity.
When designing an electrical system, one will normally need to know the current rating for the following:- Wires
- Printed Circuit Board traces, where included
- Fuses
- Circuit breakers
- All or nearly all components used
Some devices are limited by power rating, and when this power rating occurs below their current limit, it is not necessary to know the current limit to design a system. A common example of this is lightbulb holders.
[http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Ampacity]
Тематики
- электротехника, основные понятия
Синонимы
EN
DE
- Dauerstrombelastbarkeit, f
- Strombelastbarkeit, f
FR
- courant admissible, m
- courant permanent admissible, m
Немецко-русский словарь нормативно-технической терминологии > Strombelastbarkeit, f
-
20 continuous current-carrying capacity
длительная пропускная способность по току
—
[Я.Н.Лугинский, М.С.Фези-Жилинская, Ю.С.Кабиров. Англо-русский словарь по электротехнике и электроэнергетике, Москва, 1999 г.]Тематики
- электротехника, основные понятия
EN
(длительный) допустимый ток
Максимальное значение электрического тока, который может протекать длительно по проводнику, устройству или аппарату при определенных условиях без превышения определенного значения их температуры в установившемся режиме
[ ГОСТ Р МЭК 60050-826-2009]
Этот ток обозначают IZ
[ ГОСТ Р 50571. 1-2009 ( МЭК 60364-1: 2005)]EN
(continuous) current-carrying capacity
ampacity (US)
maximum value of electric current which can be carried continuously by a conductor, a device or an apparatus, under specified conditions without its steady-state temperature exceeding a specified value
[IEV number 826-11-13]
ampacity
The current in amperes that a conductor can carry continuously under the conditions of use without exceeding its temperature rating.
[National Electrical Cod]FR
courant (permanent) admissible, m
valeur maximale du courant électrique qui peut parcourir en permanence, un conducteur, un dispositif ou un appareil, sans que sa température de régime permanent, dans des conditions données, soit supérieure à la valeur spécifiée
[IEV number 826-11-13]Ampacity, the term is defined as the maximum amount of current a cable can carry before sustaining immediate or progressive deterioration. Also described as current rating or current-carrying capacity, is the RMS electric current which a device can continuously carry while remaining within its temperature rating. The ampacity of a cable depends on:
- its insulation temperature rating;
- conductor electrical properties for current;
- frequency, in the case of alternating currents;
- ability to dissipate heat, which depends on cable geometry and its surroundings;
- ambient temperature.
Electric wires have some resistance, and electric current flowing through them causes voltage drop and power dissipation, which heats the cable. Copper or aluminum can conduct a large amount of current before melting, but long before the conductors melt, their insulation would be damaged by the heat.
The ampacity for a power cable is thus based on physical and electrical properties of the material & construction of the conductor and of its insulation, ambient temperature, and environmental conditions adjacent to the cable. Having a large overall surface area may dissipate heat well if the environment can absorb the heat.
In a long run of cable, different conditions govern, and installation regulations normally specify that the most severe condition along the run governs the cable's rating. Cables run in wet or oily locations may carry a lower temperature rating than in a dry installation. Derating is necessary for multiple circuits in close proximity. When multiple cables are near, each contributes heat to the others and diminishes the amount of cooling air that can flow past the individual cables. The overall ampacity of the insulated conductors in a bundle of more than 3 must be derated, whether in a raceway or cable. Usually the de-rating factor is tabulated in a nation's wiring regulations.
Depending on the type of insulating material, common maximum allowable temperatures at the surface of the conductor are 60, 75 and 90 degrees Celsius, often with an ambient air temperature of 30°C. In the U.S., 105°C is allowed with ambient of 40°C, for larger power cables, especially those operating at more than 2 kV. Likewise, specific insulations are rated 150, 200 or 250°C.
The allowed current in cables generally needs to be decreased (derated) when the cable is covered with fireproofing material.
For example, the United States National Electric Code, Table 310-16, specifies that up to three 8 AWG copper wires having a common insulating material (THWN) in a raceway, cable, or direct burial has an ampacity of 50 A when the ambient air is 30°C, the conductor surface temperature allowed to be 75°C. A single insulated conductor in air has 70 A rating.
Ampacity rating is normally for continuous current, and short periods of overcurrent occur without harm in most cabling systems. The acceptable magnitude and duration of overcurrent is a more complex topic than ampacity.
When designing an electrical system, one will normally need to know the current rating for the following:- Wires
- Printed Circuit Board traces, where included
- Fuses
- Circuit breakers
- All or nearly all components used
Some devices are limited by power rating, and when this power rating occurs below their current limit, it is not necessary to know the current limit to design a system. A common example of this is lightbulb holders.
[http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Ampacity]
Тематики
- электротехника, основные понятия
Синонимы
EN
DE
- Dauerstrombelastbarkeit, f
- Strombelastbarkeit, f
FR
- courant admissible, m
- courant permanent admissible, m
Англо-русский словарь нормативно-технической терминологии > continuous current-carrying capacity
См. также в других словарях:
courant de surface — paviršinė srovė statusas T sritis fizika atitikmenys: angl. surface current vok. Oberflächenstrom, m rus. поверхностный ток, m pranc. courant de surface, m; courant superficiel, m … Fizikos terminų žodynas
Courant de gibraltar — Le détroit de Gibraltar séparant l Espagne et le Maroc et qui est en communication avec la mer Méditerranée et l océan Atlantique. Il y a deux courants contraires se manifestant dans celui ci: le courant de surface : nommé courant entrant… … Wikipédia en Français
Courant de Leeuwin — Pour les articles homonymes, voir Leeuwin. Fichier:Leeuwin current 1.jpg Courants en été: le courant chaud de Leeuwin est représenté par une flèche rouge descend vers le sud tandis que le courant froid des caps représenté par une flèche bleue… … Wikipédia en Français
Courant de marée — Pour les articles homonymes, voir Courant. Le raz de Sein (France) est un passage que le courant de marée rend particulièrement dangereux … Wikipédia en Français
courant superficiel — paviršinė srovė statusas T sritis fizika atitikmenys: angl. surface current vok. Oberflächenstrom, m rus. поверхностный ток, m pranc. courant de surface, m; courant superficiel, m … Fizikos terminų žodynas
surface current — paviršinė srovė statusas T sritis fizika atitikmenys: angl. surface current vok. Oberflächenstrom, m rus. поверхностный ток, m pranc. courant de surface, m; courant superficiel, m … Fizikos terminų žodynas
Courant de Gibraltar — Le détroit de Gibraltar séparant l Espagne et le Maroc et qui est en communication avec la mer Méditerranée et l océan Atlantique. Il y a deux courants contraires se manifestant dans celui ci: le courant de surface : nommé courant entrant… … Wikipédia en Français
Courant Marin — Pour les articles homonymes, voir Courant. Les principaux courants marins (carte de 1943) Un courant marin est un déplacement d … Wikipédia en Français
Courant océanique — Courant marin Pour les articles homonymes, voir Courant. Les principaux courants marins (carte de 1943) Un courant marin est un déplacement d … Wikipédia en Français
Courant electrique — Courant électrique Pour les articles homonymes, voir Courant. Un courant électrique est un déplacement d ensemble de porteurs de charge électrique, généralement des électrons, au sein d un matériau conducteur. Ces déplacements sont imposés par l… … Wikipédia en Français
Courant Électrique — Pour les articles homonymes, voir Courant. Un courant électrique est un déplacement d ensemble de porteurs de charge électrique, généralement des électrons, au sein d un matériau conducteur. Ces déplacements sont imposés par l action de la force… … Wikipédia en Français